Key Takeaways
- Industrial blenders are cornerstone equipment for achieving repeatable, high-quality products in manufacturing sectors.
- Technological innovation has introduced greater efficiency, safer operation, and lower environmental impact in blending solutions.
- A variety of blender types suit different material requirements, maximizing product outcomes.
- Routine maintenance and strict adherence to safety compliance are key to reliable blender performance and operator safety.
Industrial blending machines play a central role in numerous manufacturing operations, delivering the consistency and quality that consumers and regulatory bodies have come to expect. Modern production lines rely on these robust solutions for efficiency, product integrity, and safe output across a wide array of industries. As technology has evolved, so too have the features and capabilities of the industrial mixer, ensuring manufacturers can meet increasingly exacting standards in today’s competitive market.
The shift toward automation, safety, and sustainability in industrial blending technology has revolutionized how businesses operate. Now, blending equipment features state-of-the-art controls, enhanced safety assurances, and increased energy efficiency, all while being adaptable for specialized production requirements. This article examines the crucial roles, advancements, and future directions for industrial blenders, enabling manufacturers to make informed and effective decisions.
Types of Industrial Blenders
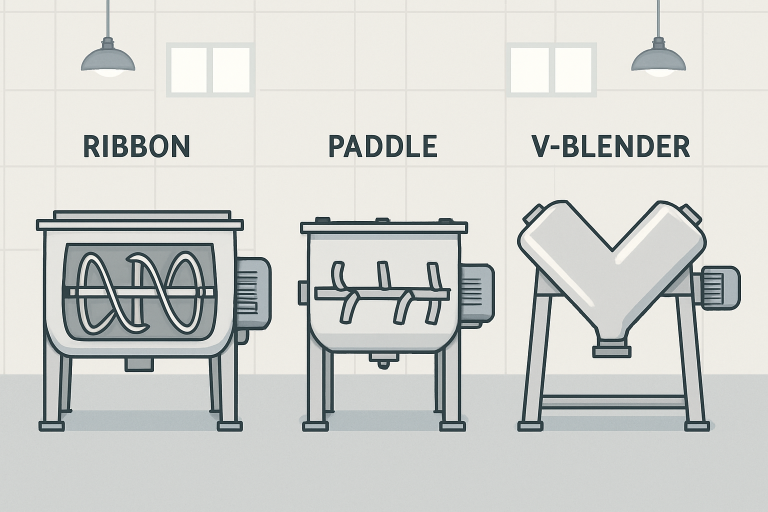
Industrial blending machines are engineered in a variety of designs tailored to the specific consistency, sensitivity, and rheological requirements of different materials:
- Ribbon Blenders: Recognized for their helical ribbons, these blenders create a counteracting mixing action that ensures thorough distribution in dry powders and granules.
- Paddle Blenders: Paddle-equipped designs gently and thoroughly mix material, providing an ideal solution for delicate substances that must retain their structural integrity during the mixing process.
- V-Blenders: With their distinctive V-shaped chambers, these blenders are typically used for dry powders where homogeneity and short blending times are essential.
Technological Advancements in Blending Machines
The technological growth in industrial blenders has unlocked new standards in manufacturing reliability and innovation. Automation and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) now allow operators to set, monitor, and adjust mixing cycles with exceptional precision, ensuring repeatable results. High-efficiency motors and variable-speed drives optimize energy use while still meeting rigorous process needs, thereby limiting operational costs and the facility’s carbon footprint.
- Automation and Control Systems: Smart controls provide real-time feedback and analytics, resulting in significant improvements in batch-to-batch consistency and traceable quality assurance.
- Energy Efficiency: Advanced mechanical and electrical designs minimize energy loss, aligning with stricter industry and environmental standards.
- Safety Features: Modern blending machines now integrate advanced guarding, emergency stop protocols, and user-friendly cleaning designs, protecting personnel and meeting legal safety requirements, as highlighted by safety authorities such as OSHA.
Applications Across Industries
The adaptability and design variations of industrial blenders make them critical in diverse markets, each with unique formulation and regulatory demands:
- Food and Beverage: These industries rely on blending machines to ensure consistency, texture, and safety in products such as spice blends, bakery mixes, and sauces.
- Pharmaceuticals: Blenders are vital for combining active pharmaceutical ingredients and excipients to maintain dose uniformity and compliance with health regulations.
- Chemicals: In chemical manufacturing, blenders ensure the homogeneity of raw components, which is crucial for reproducible chemical reactions and the quality of the final product.
- Cosmetics: Consistent blending delivers smooth, stable products such as creams, lotions, and makeup while maintaining the gentle handling often required by high-value or sensitive ingredients.
Maintenance and Safety Considerations
Preventative maintenance and proactive safety measures are non-negotiable for sustaining equipment performance and operator welfare. Scheduled inspections can detect early signs of wear or misalignment before they lead to breakdowns. At the same time, adherence to cleaning protocols reduces the risk of cross-contamination—especially crucial in food and pharmaceutical facilities.
- Routine inspections enable the detection and correction of potential faults or excess wear.
- Cleaning schedules and procedures help maintain hygiene and product purity.
- Operator training in safety, emergency shutdown procedures, and equipment-specific operations fosters a safer work environment and promotes proper machine handling.
Future Trends in Industrial Blending
The future of industrial blending lies in a blend of connectivity, customization, and environmental responsibility. The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) is enabling predictive maintenance and more refined control through real-time monitoring and data analytics. Trends show a shift toward more customizable homogeneity solutions, driven by specialized industry requirements ranging from micro-batch processing to allergen-free production.
- Integration of IoT: Machine connectivity allows real-time tracking of equipment health and process parameters, leading to data-driven maintenance decisions and reduced unscheduled downtime.
- Customization: Manufacturers are increasingly demanding blenders tailored for specific applications, resulting in greater flexibility, modularity, and smart integration options.
- Sustainability: Evolving blender designs now prioritize eco-friendly materials and energy-saving technologies, addressing both corporate and regulatory sustainability goals.
Industrial blending machines continue to drive advancements and reliability in modern manufacturing. By staying informed about emerging technologies, safety standards, and sustainability practices, manufacturers can remain competitive and deliver consistently superior products to market.






